 |
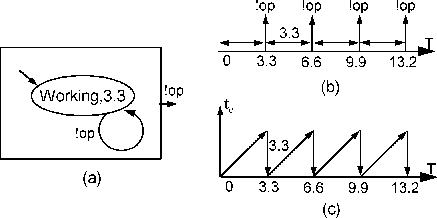
An example, Ex_Timer, shows how to define a concrete atomic
class from Atomic. In this example, we define a class
SimplestTimer which generates an output, op, every
3.3 seconds as illustrated in Figure 3.1.
SimplestTimer has one output port, op. In the
constructor, op is assigned by calling AddOP. The
function init() does nothing because the class has no
internal variable. The function tau() returns 3.3 all the
time.
class SimplestTimer: public Atomic {
public:
OutputPort* op;
SimplestTimer(const string& name=""): Atomic(name), n(0)
{ op = AddOP("op"); }
/*virtual*/ void init(){}
/*virtual*/ Time tau() const {
return 3.3;
}
Since there is no input transition defined, delta_x has the
null body. However, delta_y returns the output op.
/*virtual*/ bool delta_x(const PortValue& x) {return false;}
/*virtual*/ void delta_y(PortValue& y)
{
y.Set(op);
}
The display function Get_s() returns the current status,
which is constantly Working.
/*virtual*/ string Get_s() const {
return string("Working");
}
};
If you try step, you can see the animation is increasing the
elapsed time. The following display shows the state at time
2.188 where the schedule time t_s=3.3 and
the elapsed time t_e=2.188.
(STimer:Working, t_s=3.300, t_e=2.188) at 2.188
The simulation run will stop at 3.3 because its run mode is
step-by-step when using step. At that time, it will display
the discrete state transition as follows.
(STimer:Working, t_s=3.300, t_e=3.300)
--({!STimer.op},t_c=3.3)-->
(STimer:Working, t_s=3.300, t_e=0.000)
The first state is the source of state transition. An arc shows a
triggering event which is the output op of STimer at
the current time=3.3. The second state is the destination of the
state transition in which the lifespan is also 3.3 but the elapsed
time has been reset to zero.
Ex_Timer.
te to
tr by applying the command dtmode. Then preset the
simulation ending time to ``5'' by pause_at 5. Now
run until the simulation stops. When it stops at
t_c=5, print the total state using pinrt with option
q. What are the values of t_s and t_r,
respectively? Guess the value of t_e at this moment.
int n in
SimplestTimer class. n should be set = zero in
init(), and it should increase by one in delta_y().
Get_s() shows n in the C print format of
"Working, n=%d" .